Lazart : Laser Attack and Robustness
Lazart is a tool based on concolic
execution that evaluates the robustness of LLVM code
against multi- fault attacks.
Lazart is an academic project developed at VERIMAG
laboratory, at the University of Grenoble-Alpes,
France. Its development has been supported by two
projects: the Sertif
project (project ANR-14-ASTR-0003-01) and The
FUI SecurIoT project (2017-2020).
Lazart is a high level tool targeting developers and
auditors. It allows to identify vulnerable paths et
could be used to evaluate the accuracy of
countermeasures, relatively to a given faul model. The
particularies of Lazart are the following ones :
- Lazart takes into account multi-faults, according to the state of the art in attacks. Multi-fault is also a way to encompass low-level attacks.
- Lazart is based on a (efficient) concolic engine, Klee, allowing to establish correctness results (relatively to a given fault model)
- Attacks scenarios characterizing successful
attacks are stated by assertions. Combining attack
scenarios and fault models give a flexible way to
evaluate codes and countermeasures.
3 fault models are supported:
- Test inversion (modification of the branch resulting on the evaluation f a condition). It is a very powerful fault model that encompasses several low-level fault models (nopping a JUMP, modifying a register, modifying the arget of a JMP ...)
- Modification of value that are read. This a
classical volatile data modification fault model.
Thanks to the symbolic engine, value can be chosen
by Lazart.
- No execution of a call. This fault model corresponds to classical attacks where we try to not consider the result of a function (for instance a new random number)
We are currently developing a new version of Lazart
allowing to efficently combine fault models and
attacks scenarios.
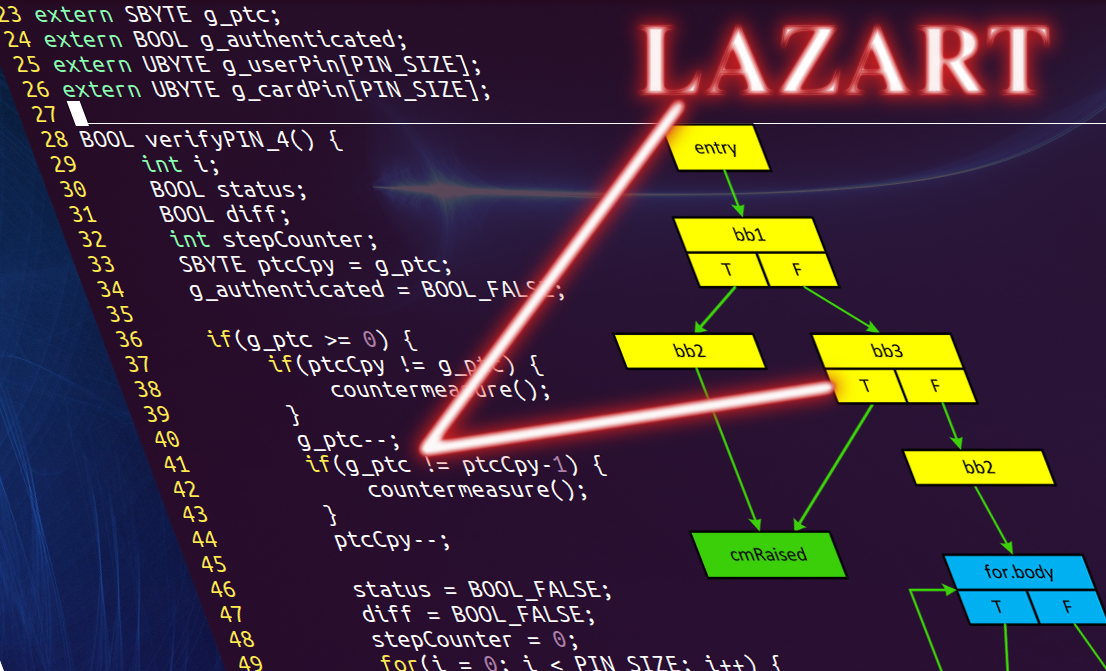
Results on an example
Here is an example of verify-pin with attacks against
authentication. We aim a maximum of 4 faults:
- the source code: Verify-pin2
- number of founded attacks : out.txt
- attacks scenarios:
fault_graph_appli_1_test_test000011.replay.pdf
(with a single fault injection)
fault_graph_appli_1_test_test000012.replay.pdf
(with a single fault injection)
fault_graph_appli_2_test_test000006.replay.pdf
(with a double fault injection)
fault_graph_appli_4_test_test000017.replay.pdf (with four fault
injections)
More examples can be found in the FISSC
collection
Publications about Lazart:
Guilhem Lacombe, David Feliot, Etienne Boespflug, Marie-Laure Potet.Combining Static Analysis and Dynamic Symbolic Execution in a Toolchain to detect Fault Injection Vulnerabilities. Journal of Cryptographic Engineering 2023.
Guilhem Lacombe, David Feliot, Etienne Boespflug, Marie-Laure Potet.
Combining Static Analysis and Dynamic Symbolic Execution in a Toolchain to detect Fault Injection Vulnerabilities. PROOFS 2021. (examples sources)
Etienne Boespflug, Cristian Ene, Laurent Mounier, Marie-Laure Potet.
Countermeasures Optimization in Multiple-Fault Injection Context. Fault Diagnosis and Tolerance in Cryptography 2020. (examples sources)
Marie-Laure Potet, Laurent Mounier, Maxime Puys and Louis Dureuil.
Lazart: a symbolic approach to evaluate the impact of fault injections by test inverting.
ICST 2014, International Conference on Software Testing.
Lionel Rivière and Marie-Laure Potet and Thanh-Ha Le
and Julien Bringer and Hervè Chabanne and Thanh-Ha Le
and
Maxime Puys. Combining High-Level and Low-Level
Approaches to Evaluate Software Implementations
Robustness Against Multiple Fault Injection Attacks.
International Symposium on Foundations and Practice of
Security, FPS 2014,
Lecture Notes in Computer Science.
FISSC: a Fault Injection and Simulation Secure Collection.
In International Conference on Computer Safety, Reliability and Security (SAFECOMP), 2016.
If you are interested for more information please contact etienne.boespflug(at)univ-grenoble-alpes.fr or Marie-Laure.Potet@univ-grenoble-alpes.fr
APP depot link here.